A Deep Dive into Twitter’s Censorship Complex
In a world increasingly governed by opaque institutions, the issue of censorship and control of information has come to the forefront, especially as more of our societal discourse moves onto platforms like Twitter. The “Twitter Files,” released after Elon Musk’s acquisition of the company in 2022, are a manifestation of that opacity finally being peeled back. These files, made available to select journalists, provide a disturbing look into the vast and intertwined network of government agencies, private corporations, and political actors who had unprecedented influence over Twitter’s content moderation policies.
The Twitter Files reveal a systemic structure where Twitter was frequently manipulated or coerced into suppressing viewpoints, censoring content, and restricting accounts in ways that aligned with specific political agendas. Let’s dig deeper into what this means for our understanding of free speech and institutional power.
LINK TO JUDICIARY HEARING REPORT
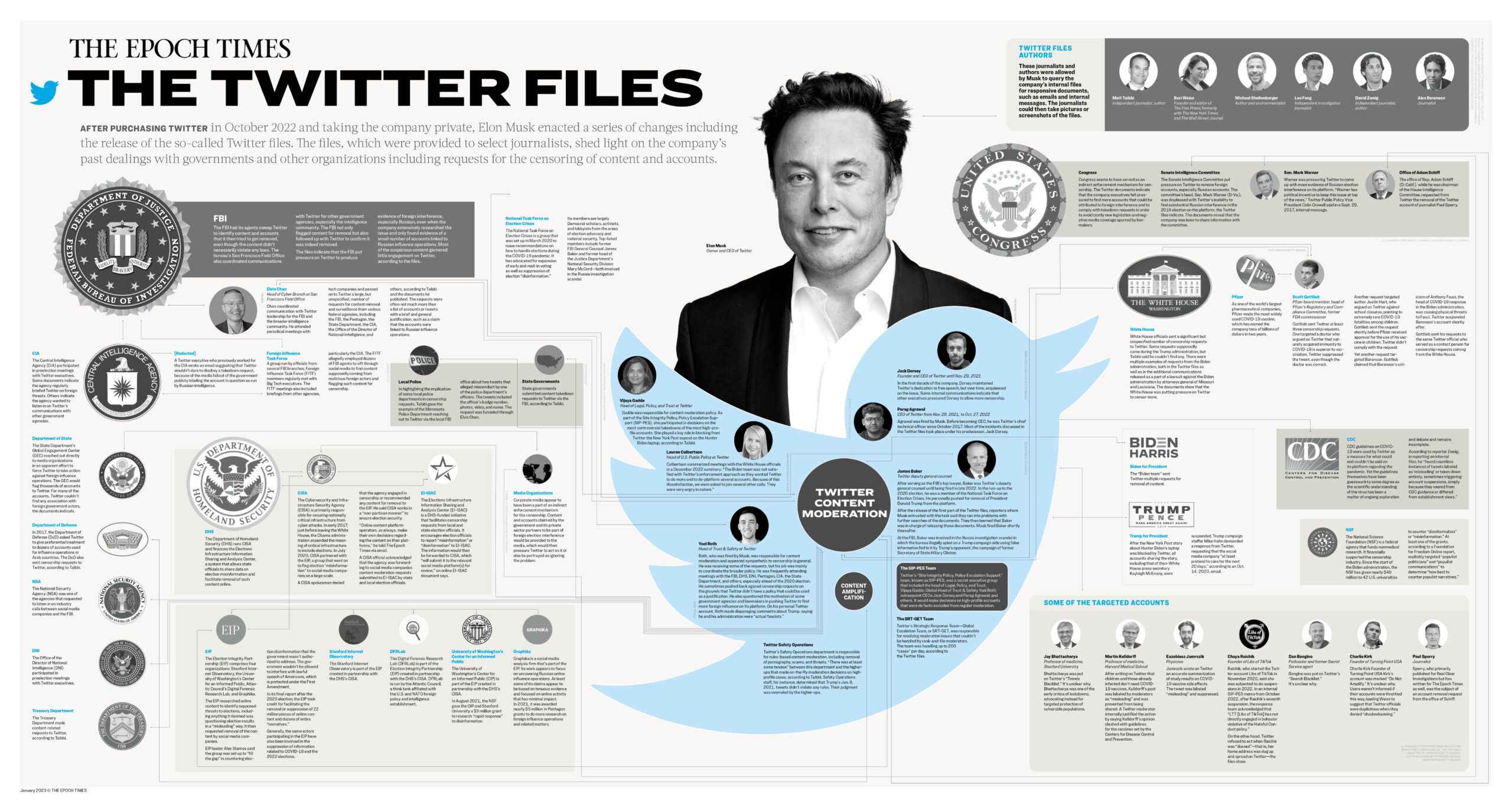
When people hear “censorship,” the first thought may be that it’s a function of authoritarian governments or rogue actors. However, the Twitter Files reveal something far more sophisticated: a collaborative effort between Twitter and various U.S. government agencies, including the FBI, Department of Homeland Security (DHS), and even the CIA.
The FBI’s role, for instance, was not confined to national security issues. Under the guise of handling disinformation campaigns and foreign influence operations, the Bureau had a direct line to Twitter’s moderation team. Communications between these agencies and Twitter reveal that the FBI was regularly flagging specific tweets and accounts for “misinformation” or “potential harm,” nudging the platform to censor content without formal legal processes. Notably, these requests often targeted not just foreign state actors, but American citizens and journalists as well.
The Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) also played a significant role. The files point to a situation where CISA coordinated with Twitter to monitor, assess, and even flag domestic narratives on topics ranging from election integrity to COVID-19, working closely with various public and private partners.
The Private Sector’s Role: Corporate Collusion and Big Pharma’s Agenda
The files also reveal an unholy alliance between Twitter and private corporations. Pfizer, one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world, was found to have exerted influence over the platform’s moderation practices, especially as it pertained to COVID-19 vaccine-related discussions. Messages between Pfizer representatives and Twitter executives indicate that the company was keen on limiting any public skepticism or critique regarding vaccine efficacy and safety.
This relationship highlights a disturbing dynamic where economic powerhouses in the pharmaceutical industry could suppress dissent or criticism under the guise of “misinformation,” in a way that aligned directly with their profit motives. Such censorship of content was not always clearly labeled, and many voices questioning vaccine mandates or the data were silenced without much public knowledge.
Moderation as Policy: The Political Arms of Censorship
Beyond corporate and governmental pressures, the Twitter Files reveal a far-reaching collusion with political bodies that worked actively to censor dissenting views, often without a clear legal basis. Under the Biden administration, there were increasing pressures on the platform to moderate content that was seen as damaging to the public’s perception of the administration’s policies, particularly around elections and public health.
One example of this is the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP), which was reportedly responsible for flagging large volumes of content related to the 2020 presidential election. While election security is a legitimate concern, the EIP’s role in censorship illustrates a broader problem: the definition of “misinformation” often morphs into a convenient tool to silence legitimate questions or debates that don’t fit the preferred narrative.
What’s fascinating, yet unsurprising, is that this phenomenon did not only happen under the Biden administration. The files show that during the Trump administration, political operatives were also communicating with Twitter to suppress certain types of content. The Trump administration’s efforts were less successful, but they reveal that no political party is above leveraging these tools of suppression when it benefits them.
The Network of ‘Trusted’ Moderators: From Government to the CDC
It is easy to overlook how intertwined various bureaucratic institutions have become with the business of controlling online discourse. The files show that Twitter was engaged in frequent conversations with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), particularly in the management of COVID-19-related content. As new findings emerged, the platform’s content moderation policies often aligned directly with the CDC’s messaging. What constitutes “misinformation” seemed more aligned with bureaucratic consensus than actual evolving science.
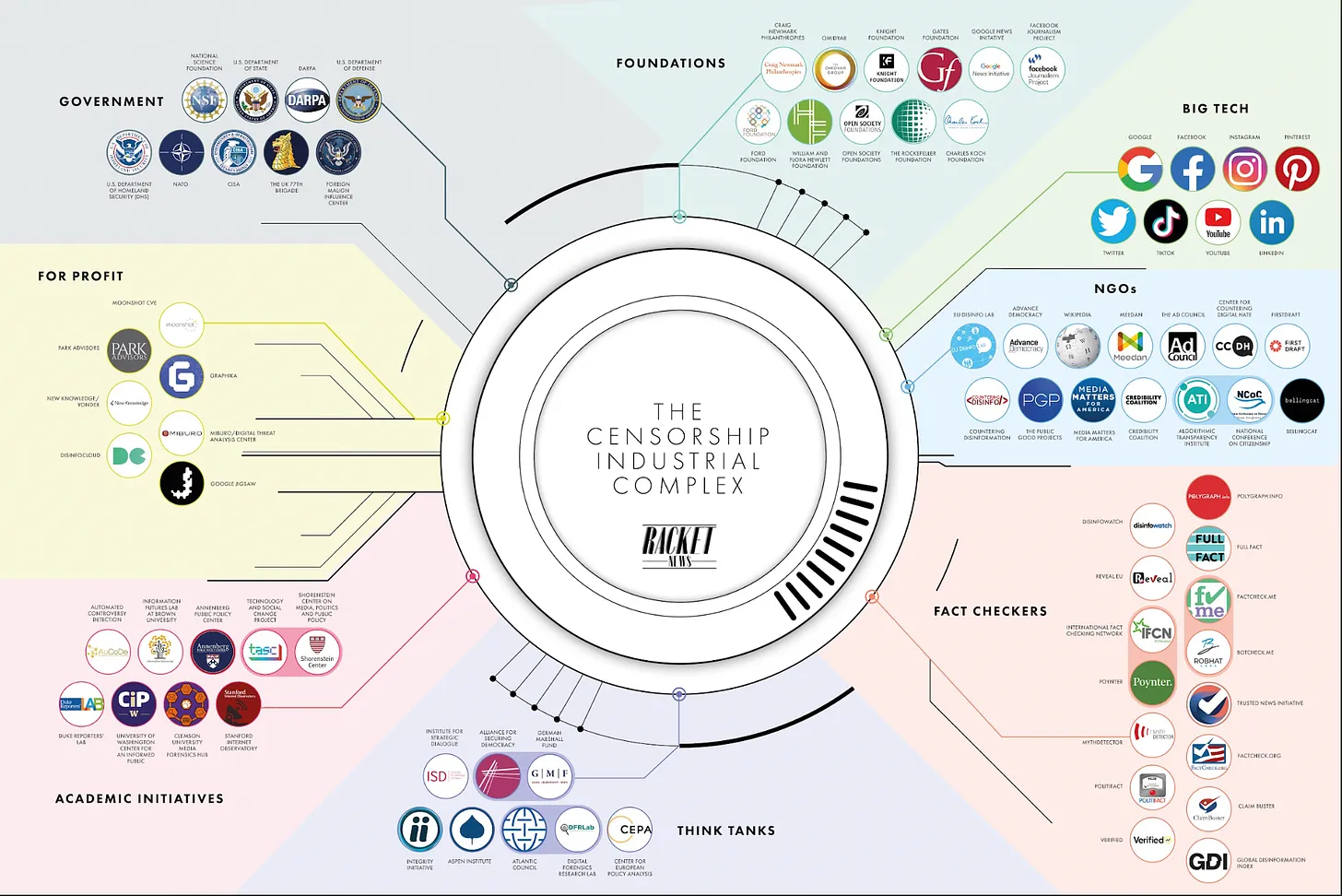
In addition, the files disclose collaborations with entities like the Department of State’s Global Engagement Center, which was tasked with countering foreign disinformation. While that mission sounds noble, it also opened up a door to quieting internal dissent within the U. S. itself. This raises fundamental questions about the balance of power and how much sway government organizations should have in the moderation decisions of private companies. Moreover, the influence of government entities on private companies might inadvertently lead to a chilling effect on free speech and public discourse, as the lines between countering disinformation and stifling dissent blur. This scenario is particularly concerning when considering the landscape of media consumption dominated by just 6 corporations controlling media consumption, which can amplify these issues further. As these corporations play a crucial role in shaping narratives, it becomes imperative to scrutinize the extent of governmental influence they allow in guiding their content moderation policies.
The ‘Twitter Files’ Journalists: Gatekeepers of Truth or Pawns in the Game?
Much of the responsibility for these revelations was given to a group of journalists: Matt Taibbi, Bari Weiss, Michael Shellenberger, and others. They were provided access to a trove of internal documents and tasked with making sense of Twitter’s moderation machinery. In a sense, these journalists became gatekeepers of this information, releasing select portions of the files to the public.
This transparency project has had its share of critics, however. Some argue that the selective release of information still leaves large gaps in understanding the true scope of Twitter’s censorship apparatus. But the revelations we do have are deeply troubling and suggest a fundamental shift in how we should think about free speech in the digital age.
Conclusion: The Future of Speech in the Algorithmic Age
So, what do we make of all this? The Twitter Files provide a disturbing look at how power—whether governmental, corporate, or political—coopts platforms of public discourse to control narratives and suppress opposition. Twitter, once seen as a bastion of free speech, turns out to be another arm of institutional gatekeeping, moderating content under various pretexts but often swayed by external pressures. This revelation raises critical questions about accountability and transparency in social media governance. As we examine Twitter’s role in platform governance, it becomes evident that the mechanisms of power and influence can significantly distort the essential functions of communication and debate. Ultimately, the implications of the Twitter Files underscore the urgent need for a reevaluation of how social media platforms operate and the ethical responsibilities they bear in fostering genuine discourse.
The implications are profound. As we move forward, it becomes clearer that any significant platform is vulnerable to this type of influence. The real question is whether future platforms, under Musk’s leadership or otherwise, will break away from these ties or continue to operate under the thumb of vested interests. For now, what we can say for certain is this: censorship isn’t always an authoritarian brute force; it is, more often than not, a sleek, bureaucratic machine, finely tuned to silence dissent while keeping its image clean.
In the end, the Twitter Files are not just about Twitter. They’re about us—about how much we are willing to tolerate the suppression of ideas under the guise of moderation and “safety,” and how we can ensure that free speech remains at the core of our democratic ideals in a world increasingly governed by algorithms, influence, and behind-the-scenes power plays.
What was Unveiled by the Twitter Files:
Government Influence:
- FBI: Direct involvement in flagging tweets and accounts for content moderation, often outside legal processes, focusing on “misinformation” and “potential harm.”
- DHS (Department of Homeland Security): Played a role in monitoring and flagging domestic narratives, particularly related to election integrity and COVID-19, coordinating with Twitter through the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
- CIA: Had a hand in influencing certain moderation practices, with implications in foreign and domestic narratives.
- EIP (Election Integrity Partnership): Actively flagged content around the 2020 presidential election, blurring the lines between election security and censorship.
Corporate Collusion:
- Pfizer: Pressured Twitter to limit public skepticism regarding vaccine efficacy and safety, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Private Sector Influence: Corporations like Pfizer had a say in shaping moderation policies that aligned with their business interests, specifically targeting COVID-19-related discussions.
Political Pressure:
- Biden Administration: Actively engaged in pushing Twitter to censor content that conflicted with its political agenda, particularly around elections and public health.
- Trump Administration: Also attempted to influence Twitter’s content moderation, although these efforts were reportedly less successful than those of the Biden administration.
Public Health and Scientific Narratives:
- CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention): Collaborated with Twitter to control COVID-19-related content, suppressing narratives that didn’t align with the CDC’s official stance.
- Pfizer and Other Health Organizations: Engaged in censorship efforts to stifle dissent or criticism of their products and policies, particularly during the pandemic.
Foreign Influence Operations:
- State Department’s Global Engagement Center: Tasked with countering foreign disinformation but also contributed to silencing domestic dissent, widening the scope of content suppression.
Media and Information Control:
- Election Misinformation: Disinformation narratives became a catch-all for censoring any content that didn’t conform to established political or institutional agendas during the 2020 election.
- COVID-19 Misinformation: Heavy-handed content moderation policies were put in place to curtail discussions around COVID-19, including dissenting scientific voices.
Twitter’s Internal Moderation System:
- Content Moderation Team: Operated in direct communication with government agencies, the private sector, and political actors, ensuring specific narratives were pushed and others were suppressed.
- Safety Operations Team: Responsible for implementing the moderation decisions, including restricting or suspending accounts flagged by external partners.
Journalistic Control of Information:
- Selective Release of Information: Journalists chosen to handle the Twitter Files, like Matt Taibbi and Bari Weiss, were given access to internal documents, raising questions about the full transparency of the files and the curation of what was released to the public.







